C Control Statements Test 3. C control statements test paper 3 contains questions from decision statement: if-else and switch, loop statement: for loop, while loop & do-while loop and jump statement: break and continue. 11) Which statements are correct about an if-else statement in a C-program? Nested if-else statements are allowed. Output is as: Enter the three Ages of Ram,Sham and Ajay 14 17 19 Ram is Youngest. Ladder if or else if statement When in a complex problem number of condition arise in a sequence, then we can use Ladder-if or else if statement to solve the problem in a simple manner. The continue statement skips the current iteration of the loop and continues with the next iteration. Its syntax is: continue; The continue statement is almost always used with the if.else statement. Aug 21, 2020 - In World Tech Blog Site you can get information about Technology, computer Language, programming, IT field, future technology, trending programming language and technology. Conditional statements. Within a method, we can alter the flow of control (the order in which statements are executed) using either conditionals or loops. The conditional statements if, if-else, and switch allow us to choose which statement will be executed next. Each choice or decision is based on the value of.
- Operator In C Language
- If Else C++ Sample Program
- If Else Statement In C Language Ppt Presentations
- If Else Statement In C Language Ppt Presentation
C control statements test paper 3 contains questions from decision statement: if-else and switch, loop statement: for loop, while loop & do-while loop and jump statement: break and continue.
11) Which statements are correct about an if-else statement in a C-program?
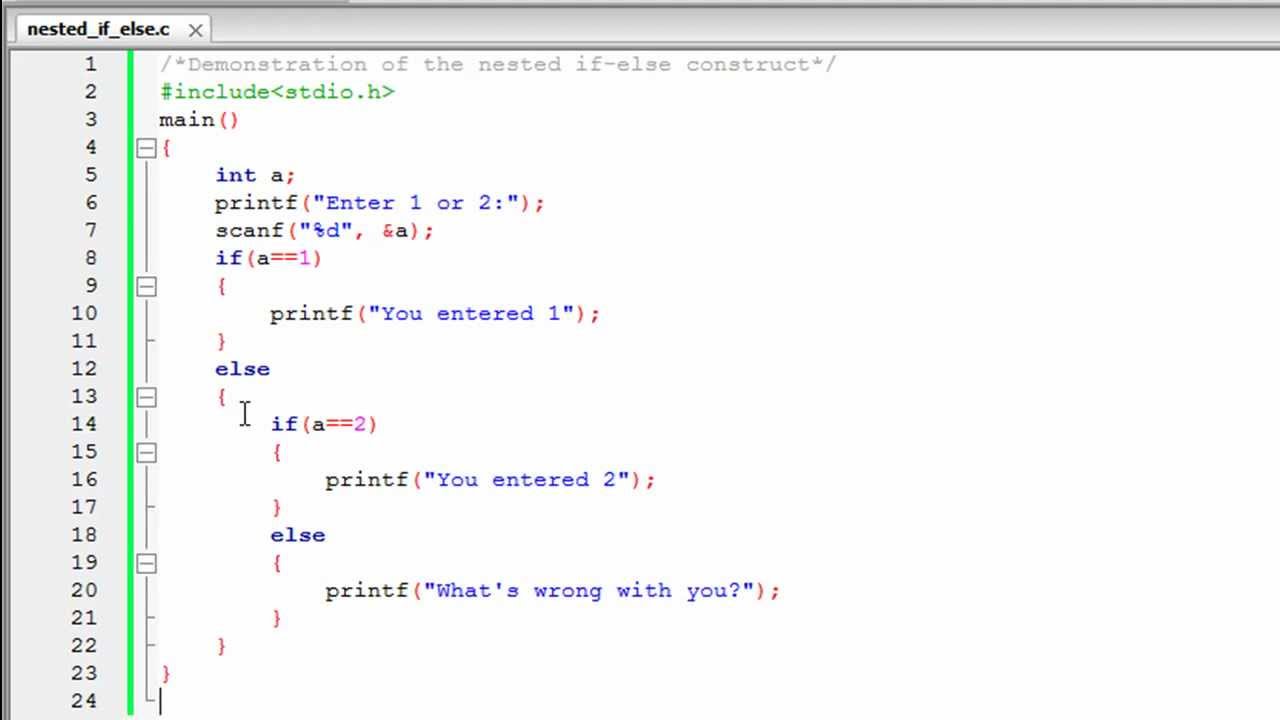
- Nested if-else statements are allowed
- Every if-else statement can be replaced by an equivalent statement using ?: operators
- Multiple statement in else block are allowed
- Multiple statement in if block are allowed
- 1, 3 and 4
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
- 2 , 3and 4
- 1 and 4
The correct option is (a).
Explanation:
Nested if-else statement is allowed in C-program we can use if-else statement within if or else statement.
Multiple statements in if or else block are allowed because we can execute multiple statements against true value of if or else condition by placing the statements within { ?.. }.
Mostly if-else statement can be replaced by ternary operator but there are some exceptions also in which if-else statement cannot be replaced by ternary operator.
Therefore 1, 3 and 4 statements are correct about if-else statement.
12) Find out the error, if any in the below program?
- Error: Constant expression required at line case P:
- Error: There is no break statement in each case
- Error: No default value is specified
- No error
The correct option is (a).
Explanation:
On compiling the program compiler will report an error 'constant expression required' in the line case P: because variable name is not allowed to be used with case statements.
The case statements only accept constant expression. Therefore the Error: Constant expression required at line case P: is occur.
13) Find out the error, if any in the below program?
- Error: in switch statement
- Error: in case 1*2+4 statement
- Error: No default specified
- No Error
The correct option is (d).
Explanation:
In switch statement constant expression are allowed therefore in case 1*2+4 statement it will give no error.
Therefore it prints 'Case1' in the output of program.
14) A long integer is at least 32 bits wide and a short integer is at least 16 bits wide
- True
- False
The correct option is (a).
Explanation:
The basic C compiler used is 16 bit compiler, below are the size of their data types:
The size of long int is 4 bytes wide i.e. 32 bits.
The size of short int is 2 bytes wide i.e. 16 bits

15) A char variable can store either a Unicode character or an ASCII character.
- True
- False
The correct option is (a).
Explanation:
Yes, char variable is allowed to store either a Unicode character or an ASCII character because encoding of character data type is done in Unicode or ASCII format.
| Language | ||||
| Standard Library Headers | ||||
| Freestanding and hosted implementations | ||||
| Named requirements | ||||
| Language support library | ||||
| Concepts library(C++20) | ||||
| Diagnostics library | ||||
| Utilities library | ||||
| Strings library | ||||
| Containers library | ||||
| Iterators library | ||||
| Ranges library(C++20) | ||||
| Algorithms library | ||||
| Numerics library | ||||
| Localizations library | ||||
| Input/output library | ||||
| Filesystem library(C++17) | ||||
| Regular expressions library(C++11) | ||||
| Atomic operations library(C++11) | ||||
| Thread support library(C++11) | ||||
| Technical Specifications |
| Labels | ||||
| label : statement | ||||
| Expression statements | ||||
| expression ; | ||||
| Compound statements | ||||
| { statement... } | ||||
| Selection statements | ||||
| if | ||||
| switch | ||||
| Iteration statements | ||||
| while | ||||
| do-while | ||||
| for | ||||
| range for(C++11) | ||||
| Jump statements | ||||
| break | ||||
| continue | ||||
| return | ||||
| goto | ||||
| Declaration statements | ||||
| declaration ; | ||||
| Try blocks | ||||
| try compound-statementhandler-sequence | ||||
| Transactional memory | ||||
synchronized, atomic_commit, etc(TM TS) |
Conditionally executes another statement.
Used where code needs to be executed based on a run-time or compile-time condition.
|
[edit]Syntax
attr(optional)if(condition)statement-true | (until C++17) |
attr(optional)if(condition)statement-trueelsestatement-false | (until C++17) |
attr(optional)ifconstexpr(optional)(init-statement(optional)condition)statement-true | (since C++17) |
attr(optional)ifconstexpr(optional)(init-statement(optional)condition)statement-trueelsestatement-false | (since C++17) |
| attr(C++11) | - | any number of attributes |
| condition | - | one of
|
| init-statement(C++17) | - | either
|
| statement-true | - | any statement (often a compound statement), which is executed if condition evaluates to true |
| statement-false | - | any statement (often a compound statement), which is executed if condition evaluates to false |
[edit]Explanation
If the condition yields true after conversion to bool, statement-true is executed.
If the else part of the if statement is present and condition yields false after conversion to bool, statement-false is executed.
In the second form of if statement (the one including else), if statement-true is also an if statement then that inner if statement must contain an else part as well (in other words, in nested if-statements, the else is associated with the closest if that doesn't have an else)
Output:
If Statements with InitializerIf init-statement is used, the if statement is equivalent to
or
Except that names declared by the init-statement (if init-statement is a declaration) and names declared by condition (if condition is a declaration) are in the same scope, which is also the scope of both statements. | (since C++17) |
Constexpr IfThe statement that begins with In a constexpr if statement, the value of condition must be a contextually converted constant expression of type The return statements in a discarded statement do not participate in function return type deduction: The discarded statement can odr-use a variable that is not defined If a constexpr if statement appears inside a templated entity, and if condition is not value-dependent after instantiation, the discarded statement is not instantiated when the enclosing template is instantiated . Outside a template, a discarded statement is fully checked. ifconstexpr is not a substitute for the #if preprocessing directive:
Note: the discarded statement can't be ill-formed for every possible specialization: The common workaround for such a catch-all statement is a type-dependent expression that is always false: Labels (goto targets, | (since C++17) |
[edit]Notes
If statement_true or statement_false is not a compound statement, it is treated as if it were:
is the same as
The scope of the name introduced by condition, if it is a declaration, is the combined scope of both statements' bodies:
If statement-true is entered by goto or longjmp, statement_false is not executed.
| (since C++17) |
[edit]Keywords
if,else,constexpr
Operator In C Language
[edit]Defect reports
The following behavior-changing defect reports were applied retroactively to previously published C++ standards.
| DR | Applied to | Behavior as published | Correct behavior |
|---|---|---|---|
| CWG 631 | C++98 | the control flow was unspecified if first substatement is reached via a label | same as in C |
If Else C++ Sample Program
[edit]See also
If Else Statement In C Language Ppt Presentations
C documentation for if statement |
If Else Statement In C Language Ppt Presentation
