OEM factory Cummins ISB (6.7 liter) engine service manual.
Covers mechanical troubleshooting, repair, overhaul, torque specs, valve lash specs, etc. for this engine.
- 6.7 Cummins Flywheel Torque Specs Specifications
- 6.7 Cummins Flywheel Torque Specs Diagram
- 6.7 Cummins Flywheel Torque Specs 70 Gto Engine
- 6.7 Cummins Flywheel Torque Specs
- 6.7 Cummins Bolt Torque Specs

Engines: Cummins ISB 6.7 Engine
Engine Control Module: 2150
This manual does not cover the engine control system; that information can be found here:
Cummins ISB / ISC / ISL Electronic Troubleshooting Manual (CM2150)
Manual Contents
- Introduction
- Familiarization
- Air intake system overview & flow diagram
- Complete engine overview & info
- Compressed air system & flow diagram
- Cooling system overview & flow diagram
- Cylinder block overview & info
- Engine electrical equipment overview
- Engine testing overview including dyno testing
- Flow diagram for exhaust system
- Fuel system overview & flow diagram
- Cummins Accumulator Pump System (CAPS) operation
- Injectors & fuel line overview including operation theory
- Lubrication system overview & flow diagram
Troubleshooting Symptoms
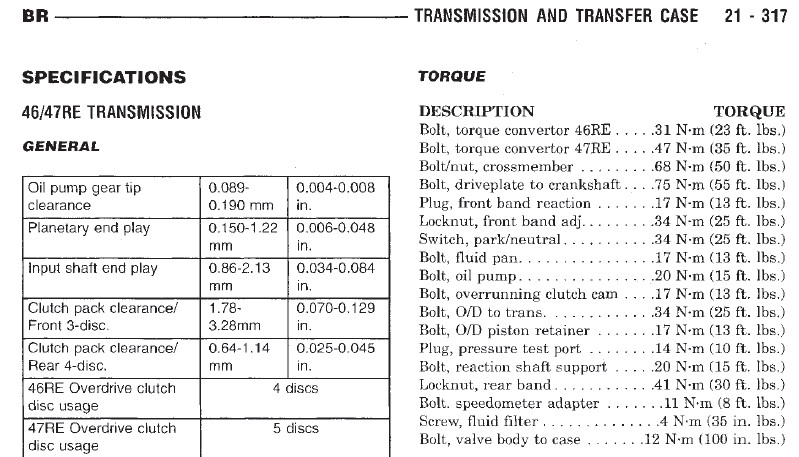
6.7 Cummins Flywheel Torque Specs Specifications
- TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS (RAM PICKUP) Application Ft. (N.m) Front Drive Shaft-To-Front Axle Flange Bolt 14 (19) Front Drive Shaft Flange-To-Transfer Case Flange Bolt 65 (88) Rear Drive Shaft Center Bearing-To-Crossmember Bolt 50 (68) Rear Drive Shaft Universal Joint Strap-To-Rear Axle Flange Bolt Dana Axle 22 (30) 9 1/4' Axle 14 (19).
- I am looking for torque specs for a 1999 dodge cummins 24 valve. I have bought a used dull mass flywheel for my 2007 dodge 3500 6.7 cummins diesel.
For 2020 Ford introduced the 3rd Generation 6.7L Power Stroke diesel, rated at an impressive peak 1,050 lb-ft of a torque and 475 horsepower. While the revised engine features a number of significant changes, the most noteworthy is likely its new piston design. For 2020 Ford introduced the 3rd Generation 6.7L Power Stroke diesel, rated at an impressive peak 1,050 lb-ft of a torque and 475 horsepower. While the revised engine features a number of significant. The new high-output engine boasts 400 hp and 1000 lb-ft of best-in-class torque. For RAM 2500 and 3500 (equipped with a 68RFE Auto) HP and torque have increased to 370 hp and 850 lb-ft to provide.
- Troubleshooting Procedures & Techniques
- Air compressor problems
- Alternator problems
- Cooling system problems
- Excessive crankcase blowby
- Low fuel pressure
- Engine brake problems
- Hard starting
- Engine noises
- Low power
- Misfire or runs rough
- Engine dies
- Speed surge
- Starts but dies
- Excessive vibration
- Fuel consumption
- Fuel in coolant
- Fuel in oil
- Low boost
- Excessive oil consumption
- Smoking
- Governor problems
- Troubleshooting overview
- More
Complete Engine
- Removal & Installation
- Cylinder Block
- Accessory drive seal
- Con rod bearings
- Main bearings
- Thrust bearings
- Camshaft, bushings, clearance & bearing supports
- Crankshaft inspection & servicing
- Crankshaft gears, pulley & seals
- Cylinder block, servicing, liners, liner seats, counterbore
- Gear cover accessory drive bushing
- Pistons & rings
- Con rods
- Piston cooling pipes
- Vibration damper
- Cylinder Head
- Clean / inspect
- Finishing / surfacing
- Installation / removal
- Leak / pressure test
- Head gasket general info
- Rocker Arms
- Crankcase breather
- Overhead adjusting, finishing, general info
- Rocker arm, clean, inspect & service
- Rocker cover & housing
- Special tools
- Cam Followers / Push Rods or Tubes
- Remove, clean, inspect, disassemble, assemble & install
Fuel System
- Fuel Flow, inspect & test
- Fuel pump, inspect & test
- Check valve
- High idle speed adjust
- Idle speed adjust
- Pressure regulator
- Pulsation damper
- Throttle lever & linkage
- VS throttle shaft housing
- Shut-off valve
- Service tools
- Stall speed test
- VS governor adjusting screw sealing washers & idle spring
- Injectors & Fuel Lines
- AFC no air check
- Air in fuel
- Cylinder misfire or smokes
- ECM fuel plate, fuel cooled
- Fuel drain line restriction
- Fuel filter, spin on
- Fuel inlet restriction
- Fuel supply lines
- Injector
- Service tools
- Static injector timing
Lubrication System
- Lube oil & filter analysis
- Lube oil contamination
- Lube oil cooler & transfer housing
- Dipstick & housing
- Lube oil filter, spin on
- Lube oil by-pass valve
- Lube oil filter head
- Lube oil high pressure relief valve
- Lube oil leaks
- Lube oil pan
- Lube oil pressure gauge
- Lube oil pressure regulator
- Lube oil pump
- Lube oil pump signal tube & signal tube orifice
- Lube oil system diagnostics
- Lube oil temperature gauge
- Lube oil thermostat
- Lube oil transfer tube
- Lube oil viscosity sensor
Cooling System
- Coolant filter, head & valve
- Temperature gauge
- Thermostat, housing & seal
- Vent lines
- Cooling system, servicing
- Cooling system, air or combustion gas test
- Cooling fan & water pump drive belt
- Fan clutch, electric / on-off / viscous
- Fan hub, belt driven
- Fan shroud, spacer & pulley
- Cooling fan
- Radiator, hoses & cap
- Radiator shutters
- Heat exchanger
- Sea water pump
- Water pump & idler
- Drive Units
- Accessory drive & pulley
- Accessory drive pulley wear sleeve
- Air Intake System
- Aftercooler
- Intake manifold
- Intake restriction
- Air leaks, intake & exhaust system
- Charge air cooler
- Turbocharger
- Turbocharger inspection
- Exhaust System
- Exhaust manifold, dry
- Exhaust restriction
- Compressed Air System
- Air compressor
- Carbon buil-up
- Air compressor head
- Pin bore wear
- Unloader & valve assy.
- Governor testing (compressor pumps continuously or will not pump
- Air leaks
Electrical Equipment
- Alternator
- Batteries, cables & connections
- Alternator drive belt
- Starter magnetic switch
- Starter solenoid
- Starter switch
- Starter motor
Engine Testing
- Dyno worksheet
- Engine run-in (dyno)
- Engine run-in (without dyno)
- Engine testing with dyno
- Mounting Adaptations
- Engine lifting brackets
- Engine mounts
- Support brackets
- Flywheel & ring gear
- Flywheel housing
- Miscellaneous
- Cup plugs
- Pipe plugs
- Straight thread fittings & plugs
In the off-road community engine swaps can be a touchy subject. Most of the time torque is what you’re looking for as that’s what will allow you to turn big tires at low RPMs. Because of that, Chevrolet LS engines are pretty common, especially the truck version of the LS family. But, diesel engines, specifically the 4BT Cummins, are becoming increasingly popular. It’s not just off-roaders who are using this engine. It can also be found in everything from 240SX drift cars to Mustang drag cars.
Before I tell you everything you need to know about this engine, I must first inform you of the absolute the basics of the 4BT. You can find even more 4BT information on Wikipedia.
6.7 Cummins Flywheel Torque Specs Diagram
4BT Cummins: Engine Basics
In the world of “light-duty” trucks, the 6BT Cummins, also known as the 12-valve Cummins, is legendary. The large size of the 6BT meant that it couldn’t fit in vehicles or equipment where there wasn’t a massive amount of space which is where the 4BT Cummins comes into play. The 4BT shares most of its components with the 6BT, but with two cylinders missing. The pistons, injectors, connecting rods, and valvetrain design are straight off of the 12v Cummins. Even though the 4BT is significantly shorter than the 6BT, it’s still a large engine, especially for a four-cylinder.
- Displacement: 3.9L – 292ci
- Bore: 4.02″
- Stroke: 4.72″
- Configuration: Inline Four-Cylinder
- Deck: Closed Deck
- Weight: 750+ lbs
- Cylinder Head Material: Cast Iron
- Engine Block Material: Cast Iron
- Compression Ratio: 17.5:1
- Valvetrain: OHV – 2 Valves per Cylinder
- Horsepower: 105hp (4BT) – 170hp (4BTA)
- Torque: 265lb-ft (4BT) – 420lb-ft (4BTA)
Out of the units listed above, weight is the most surprising. While most four cylinder come in around 400-600 lbs, the 4BT weighs a hefty 750+ lbs (the exact number depends on engine dressings and fluid level.) Horsepower may seem relatively low, especially for a 3.9L engine, but you must remember that the 4BT was designed for low-end torque and superb reliability. The post-1998 version, 4BTA, had a significant power bump thanks to its jump from eight to sixteen valves.
4BT Cummins: Real World Applications

Thanks to its size, power output, and mechanical fuel injection system, the 4BT can be found in a plethora of different applications. It’s not uncommon to see this engine in industrial equipment. The most common place you’ll find a 4BT is in bread trucks. These are large trucks which may have a relatively heavy payload, but have a tiny engine bay, making the 4BT the obvious choice. There is not any official list of 4BT applications, but bread trucks are definitely the most common application. Modern applications have since moved on to newer and more efficient diesel engines including the R2.8 Cummins.
4BT Cummins: Tuning Potential
The 4BT is by no means a performance engine. As we said above it was used in applications such as bread trucks and the numbers show it. Outputting a measly 105 horsepower @ 2,300 RPM and 265 lb-ft @ 1,600 RPM, it’s far from a screamer. Of course, the 6BT is also very weak straight from the factory, but with some modifications to the fuel system and fuel timing, big power can easily be achieved. The common 6BT fuel modifications apply to the 4BT, as they share the same fuel pump and injectors.
If you want big horsepower, a turbocharger upgrade is a great place to start. An HX35, HE341, or HE351 are great budget options which will flow significantly more air than the stock 4BT turbocharger at the cost of throttle response. All 4BT applications lack an intercooler which is great for packaging constraints but terrible for power. An intercooler is a great way to pick up horsepower and improve power consistency by keeping charge air temperatures lower.
As far as fueling is concerned, upgraded injectors are an excellent place to start, but are not necessary for small power increases. The P7100 fuel injection pump is the same one found in the 6BT. Sliding the Air Fuel Control assembly forward will result in power gains by adding fuel at low RPM. You can also ground down or remove the fuel plate which is what controls the maximum fueling. By sliding the AFC assembly forward and grounding down the fuel plate, you can see gains up to 100hp and 200+ ft-lbs. Fuel timing is crucial on the 4BT, so be sure to set it right, or you may have a blown engine on your hands.
Past the basic fueling mods, aftermarket governor springs are a great way to pick up power. The OEM governor springs of the P7100 pump limit the engine to 2,700rpm with de-fueling starting at 2,400rpm. Aftermarket governor springs will allow full fueling up to 3,000rpm or even 4,000rpm depending on what spring kit you purchase. It should be noted that four-cylinder engines are not as inherently balanced as six-cylinder engines, so don’t expect to rev a modified 4BT engine as high as a modified 6BT engine.
Tuning potential depends entirely upon budget, but it’s not too hard to get a 4BT up to 300 horsepower and 700lb-ft. It should be noted that the fueling modifications listed above apply only to 4BT engines with the Bosch P7100 pump. Models with the later VE-pump require different modifications. Check out DrivingLine’s P-Pump Cummins fuel modifications for more detailed information.
6.7 Cummins Flywheel Torque Specs 70 Gto Engine
4BT Cummins: Why Swap?
So from everything, I’ve told you so far, why would you want to swap a 4BT into your vehicle? If you’re able to fit a 6BT 12 valve into your vehicle, then that is probably the way better option. It’ll make more power, last just as long, and might be cheaper to buy.
The real reason you might want to swap a 4BT is for fuel mileage, and size constants. A 4BT barely fits into an XJ Cherokee with a 6″+ lift, so a 6BT is definitely out of the question for many Jeep owners. If fuel mileage is your legitimate reason for swapping, then the 1.9 TDI from VW is a far better option.
6.7 Cummins Flywheel Torque Specs
Summary
So what have we learned so far? The 4BT came in heavy duty applications such as bread trucks, it’s nearly identical to the 12-valve, it responds to modifications just like a 12-valve, and it’s incredibly reliable. Many 4BT engines have gone way past 300,000 miles.
6.7 Cummins Bolt Torque Specs
Jeep people love the 4BT because it is pretty much the best diesel that can fit inside of a Jeep other than the much less common 1.9 TDI swap. Let me know what you think of the 4BT in the comments below! Also check out our 6BT Cummins: Everything You Need to Know article!
